Page Contents
1. PURPOSE
It is established to learn bacterial endotoxin test procedure, to ensure that endotoxins are within the limits of parenteral preparations
2. SCOPE
It is applicable in the microbiology department of the Quality Control laboratory.
3. RESPONSIBILITY
Microbiologist
Quality Control Manager
4. INTRODUCTION
Pyrogen was defined by Webster as a “fever producing agent”. If pyrogens enter the circulatory system of Mammalia, fever reaction occurs including temperature rise, chill more seriously, shock or even death may occur. It will not cause any host response if pyrogen enters the digestive system. There exists a large amount of endotoxin in the intestines of human beings.
4.1 ENDOTOXIN
In 1884 gram discovered a differential staining technique. Bacteria were classified into two groups. Gram-positive bacteria (GPB) and gram-negative bacteria (GNB).
In 1889, Roussy successfully separated a crude fever-producing substance from gram-negative bacteria.
In 1892 Pfeifer discovered that vibrio possesses a second toxin
The second toxin appeared to be anchored to the bacterial cell. He proposed endotoxin to distinguish it from the Cholera Exotoxin.
4.2 GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN
They are the outermost cell wall component of gram-negative bacteria, which comprises high molecular weight lipopolysaccharide complexes, whose monomeric molecular weight is between 10,000 and 20,000 Daltons
4.3 HORSESHOE CRAB
The horseshoe crab is an ancient marine creature. Dr. Frederic Bang discovered that endotoxin from Vibrio caused the coagulation of blood of the horseshoe crab, which led to the death of the crab.
Bang collaborated with Dr. Jack Levin and developed a sensitive reagent prepared from the circulating blood cells—amoebocytes of Limulus polyphemus for detecting GNB.
4.4 AMEBOCYTE LYSATE
Nowadays, the blood of the horseshoe crab is used to prepare reagents for detecting endotoxin. The horseshoe crabs are returned to the sea alive after bled. In America, the lysate is prepared from the blood of Limulus polyphemus and it is called Limulus amebocytes Lysate(LAL). In Japan and China, the blood of tachypleus tridentatus is used to prepare lysate and is called Tachypleus amebocyte lysate.
4.5 RELATIONS BETWEEN ENDOTOXIN AND PYROGEN
Endotoxin is the key pyrogenic substance. In the modern pharmaceutical industry, pyrogen that can contaminate drugs is mainly endotoxin. Therefore to control the endotoxin contamination is able to control the pyrogen contamination. Bacterial endotoxin has replaced the rabbit test which is included in any pharmacopeia. Non-endotoxin pyrogenic substances also exist, such as some GBP can also produce pyrogen, but it is uncommon.
5. TESTING MATERIAL, EQUIPMENT, AND REAGENTS
5.1 Reagents
Licensed TAL or LAL
RSE or CSE with lot-specific Eu/ng ratio
TRW or LRW
Eu/ng ratio
Value determined by RSE/ CSE testing
COA provided by the vendor
EU/ng x ng/vial = EU/vial
EU/vial / ml/vial = EU/ml
RSE/CSE EU/ng ratios are lot specified and may change if either the LAL lot or CSE lot changes.
5.2 Accessory product
Endotoxin-free dilution tubes
Borosilicate glass tubes
Polystyrene plastic tube
Depyrogenated 10 x 75mm assay tubes
Borosilicate glass
Endotoxin-free pipette tips
Depyrogenated glass pipettes
Laboratory equipments
Dry heat incubator or water bath
Calibrated thermometer
Calibrated pipettor
Repeated pipettor
pH meter
Monitored refrigerator/freezer
Test tube racks, pipette bulbs
Dry heat oven
6. TEST METHOD OF GNB ENDOTOXIN
The test method of GNB endotoxin is the bacterial endotoxin test (BET) also called TAL or TAL test.
6.1 UNIT OF ENDOTOXIN AMOUNT
It is mentioned in two terms
Unit in terms of weight i.e., mg, ng
Unit in terms of fever producing activity unit i.e., EU (endotoxin unit), IU (international Unit) such that 1EU = 1IU
EU is mainly used in BET calculation.
7. GEL CLOT BET
7.1 TERMINOLOGY AND EXPLANATION
- BET bacterial endotoxin test
- TAL tachypleus amebocyte lysate
- LAL limulus amebocyte lysate
- RSE reference standard endotoxin, prepared by the Government organization that is in charge of the drug administration as the state reference standard.
- CSE Control standard endotoxin prepared by the TAL/LAL manufacturer and standardized against a reference standard (RSE/CSE) ratio and provided to the TAL/LAL user
- λ Sensitivity of LAL or TAL in EU/ml
- M Maximum dose per kg per hour
- K maximum allowable endotoxin per kg per hour
- EL endotoxin limit of a parenteral drug
- MVD maximum valid dilution
- MVC maximum valid concentration
- NWC negative water control
- NPC negative product control
- PWC positive water control
- PPC positive product control
- TRW or LRW TAL/LAL reagent water.
8. ENDOTOXIN LIMIT
Generally, the EL of some drugs can be found in the pharmacopeia. EL needs to be calculated only when it is not given in pharmacopeia.
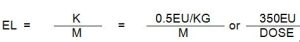
Parenterals K= 5.0EU/kg
Intrathecal, K=0.2EU/kg
Use 60 kg as the average weight of humans and 350kg as the maximum weight of the animals found in Pakistan.
8.1.1 MVC
The lowest concentration of sample that can be tested within the endotoxin limit and still achieve selected sensitivity
Use when EL is listed in units, not ml. Such as Eu/ng, Eu/U, etc.
MVC = λM/K = λ/EL
8.1.2 MVD
MVD = largest allowable dilution within the endotoxin limit that will still achieve necessary sensitivity. Use when EL is listed in ml, such as Eu/ml
MVD = EL/λ
9. RUNNING THE ASSAY
9.1 REAGENT PREPARATION AND STORAGE QUALIFICATION
9.1.1 CSE reagent rehydration
Rehydrate following lot-specific EU/ng ratio. Vortex vial for 5min for the first use and 1min for subsequent use. Vortex each dilution for at least 30 sec. Store rehydrate vial in refrigerator, not the freezer.
9.1.2 Dilutions
Dilutions can be calculated as follows
EU/ml(have) / EU/ml(want) = dilution
Example; need 2EU/ml from 16EU/ml tube. Make an 8-fold dilution.
Dilutions should be made in volumes > 2ml in case additional testing is necessary. Larger volumes appear to add stability to CSE dilutions.
9.1.3 Standard preparation for Gel Clot
Follow EU/ng ratio for vial rehydration. Prepare serial dilution to 20λ. Dilute 1:10 to get 2λ, then prepare serial 2-fold dilution to obtain λ, 1/2λ, 1/4λ. Vortex mixing is essential to keep purified endotoxin dispersed. Smaller dilution factors and larger volumes reduce error, allow stability, and allow retest.
9.2 TAL/LAL regent
Rehydrate immediately prior to testing (~ 5 min to allow to come to room temperature and dissolve). Do not vortex and cover with an endotoxin-free surface if not in use
Immediately freeze or refrigerate unused LAL.
9.3 Example
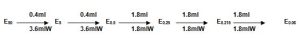
Suppose selected TAL sensitivity is λ=0.125Eu/ml, CSE is 10ng/vial
9.3.1 CSE dilution
Based on the CoA instruction, the RSE/CSE ratio of the CSE is !)EU/ng, so the endotoxin content of each vial is EU/ng X 10ng/vial = 100EU/ vial. Add 2.0ml of TRW to rehydrate CSE, vortex mix five minutes, obtain a solution of 50Eu/ml (E50). Dilute it as follows.
9.4 POSITIVE PRODUCT CONTROL
Sample test solution contains 2λ endotoxin concentration
9.4.1 Preparation
Example λ = 0.125Eu/ml
Sample concentration = 0.2mg/ml
1.0 ml E4λ + 1.0ml S0.4 —–> 2.0ml E2λ S0.2
9.5 PREPARATION, INCUBATION, AND ANALYSIS OF SAMPLES
- Run a routine assay in duplicate
- Dispense 0.1ml of standard, NWC, samples, and PPC into 10 x 75 assay tubes
- Then add 0.1m; of LAL to assay tubes
- Incubate at 37+ 1 for 1 hour + 2min.
- Invert tubes and record gelatin status.
9.6 QUALIFICATION VALIDITY, AND INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS
Verify label claim i.e., gels at 2λ, no gel at 1/4λ
NWC must not gel.
PPC must gel.
Send your technical queries about bacterial endotoxin test to get the best solution from our technical experts
FAQ:
1:What is bacterial endotoxin?
Ans: Bacterial endotoxin is a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) found in the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria.
2. What is bacterial endotoxin test procedure:
Ans: To know complete details about the endotoxin test procedure please follow all the above-mentioned steps.


