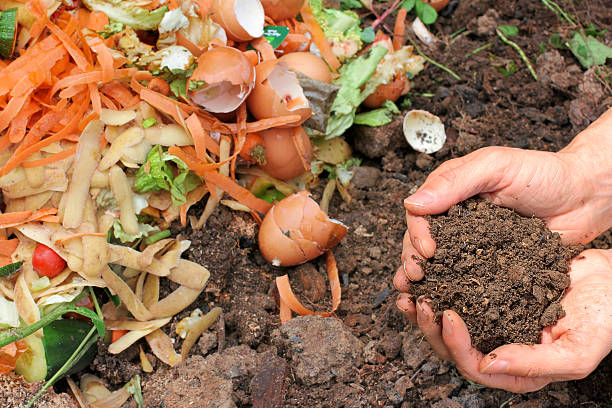
Organic compost is a type of fertilizer made from decomposed organic materials, such as leaves, food scraps, and yard waste. It enriches the soil, helping plants grow stronger and healthier. Making compost at home is a simple and eco-friendly way to reduce waste while creating a valuable resource for your garden.
Page Contents
Organic compost composition
Organic compost is typically made up of:
- Carbon-rich materials such as dead leaves, straw, and sawdust
- Nitrogen-rich materials such as food waste, grass clippings, and manure
- Air and water to support the decomposition process
- Microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and earthworms that break down the organic matter into compost
A balanced compost pile should have a carbon to nitrogen ratio of about 30:1 for efficient decomposition. The composting process takes several months, and the final product is a rich, dark soil amendment that can be used to improve soil structure and fertility.
The nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) content of organic compost can vary depending on the materials used in the composting process and the maturity of the compost.
Typically, compost contains low to moderate levels of nitrogen (1-2%),
low levels of phosphorus (0.5-1%), and moderate to high levels of potassium (2-3%).
It’s important to note that compost should not be relied upon as a sole source of nutrients for plants. It’s better to use compost as a soil amendment to improve soil structure and fertility and to supplement with other fertilizers as needed. A soil test can help determine the nutrient levels in your garden and guide fertilization decisions.
How to make organic compost at home
To make organic compost at home:
- Collect organic materials such as fruit & vegetable scraps, leaves, grass clippings, coffee grounds, and eggshells.
- Mix brown (carbon-rich) and green (nitrogen-rich) materials in a compost bin or pile.
- Keep the compost moist but not waterlogged, and turn it regularly to aerate and promote decomposition.
- Add compost accelerator like composting worms, manure, or finished compost to speed up the process.
- After several months, the compost will have decomposed into a nutrient-rich soil amendment.
- Use the finished compost in your garden or potted plants.
Organic compost accelerator
An organic compost accelerator is a substance that is added to a compost pile to speed up the decomposition process. Some examples of compost accelerators include:
- Manure: Fresh or well-aged animal manure can provide nitrogen and other nutrients to help break down organic material.
- Composting worms: Red worms and other composting worms can be added to the compost pile to help break down organic matter.
- Finished compost: Adding mature compost to a new pile can provide the beneficial microorganisms needed to get the composting process started.
- Alfalfa meal or pellets: High in nitrogen, this organic material can help balance the carbon/nitrogen ratio and speed up the decomposition process.
- Rock dust or wood ash: These materials provide essential minerals to the compost pile and can help adjust pH levels.
- Bacterial or fungal compost starters: These specially formulated products contain a mix of microbes that can jumpstart the composting process.