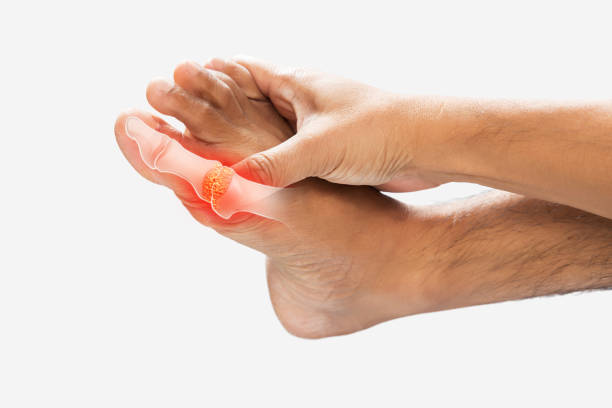
Uric acid is a waste product produced by the body after breaking down purines, which are found in certain foods and drinks. Purines are also produced by the body naturally. Uric acid is usually filtered out of the body by the kidneys and expelled through urine. However, when the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys fail to eliminate it properly, it can lead to a buildup of uric acid in the blood, resulting in various health complications. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, normal range, and treatment options for uric acid.
Page Contents
1. What is uric acid?
Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines in the body. Purines are found in certain foods and drinks, such as red meat, seafood, alcohol, and sugary drinks. When purines are broken down, uric acid is produced, which is usually filtered out of the body by the kidneys and eliminated through urine. However, if the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys fail to eliminate it properly, it can lead to hyperuricemia, a condition where there is an excessive amount of uric acid in the blood.
2. Causes of high uric acid
There are several factors that can cause an increase in uric acid levels in the blood. Some of these factors include:
- Diet: Foods high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and sugary drinks, can increase uric acid levels.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to hyperuricemia, making them more prone to developing high uric acid levels.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as gout, kidney disease, and hypothyroidism, can cause an increase in uric acid levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics and aspirin, can cause an increase in uric acid levels.
3. Symptoms of high uric acid
Hyperuricemia may not always cause symptoms, and some people may have high uric acid levels without even knowing it. However, when uric acid levels become too high, it can cause several health complications. Some of the symptoms of high uric acid levels include:
- Joint pain: High uric acid levels can cause inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Gout: Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, causing intense pain and swelling.
- Kidney stones: High uric acid levels can lead to the formation of kidney stones, which can cause severe pain and discomfort.
- Fatigue: High uric acid levels can cause fatigue and weakness, making it difficult to perform daily activities.
4. Normal range of uric acid
The normal range of uric acid in the blood can vary depending on several factors, such as age, sex, and medical history. In general, the normal range of uric acid in the blood is:
- For men: 3.4 to 7.2 mg/dL
- For women: 2.4 to 6.0 mg/dL
However, it is important to note that normal ranges can vary between different laboratories, and doctors may interpret test results differently based on the individual’s medical history and symptoms.
5. Treatment for high uric acid
The treatment for high uric acid levels depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some of the treatment options for high uric acid levels include:
- Medications: There are several medications available that can help lower uric acid levels in the blood, such as allopurinol, febuxostat, and probenecid.
- Diet and lifestyle changes: Making dietary and lifestyle changes can also be effective in managing high uric acid levels. Reducing consumption of foods high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and sugary drinks, can help decrease uric acid levels. Increasing consumption of foods that help lower uric acid levels, such as low-fat dairy products, whole grains, and fruits and vegetables, can also be helpful. Maintaining a healthy weight and staying physically active can also help manage high uric acid levels.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help flush out uric acid from the body, reducing the risk of developing kidney stones and other complications.
- Avoiding alcohol: Alcohol consumption can increase uric acid levels, so avoiding or limiting alcohol intake can be helpful in managing high uric acid levels.
- Treating underlying medical conditions: Treating underlying medical conditions, such as kidney disease or hypothyroidism, can help manage high uric acid levels.
It is important to note that while there are several treatment options available for high uric acid levels, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or making significant dietary or lifestyle changes.
6. Conclusion
Uric acid is a waste product produced by the body after breaking down purines, which are found in certain foods and drinks. When the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys fail to eliminate it properly, it can lead to hyperuricemia, a condition where there is an excessive amount of uric acid in the blood. High uric acid levels can cause several health complications, such as joint pain, gout, kidney stones, and fatigue.
The normal range of uric acid in the blood can vary depending on several factors, such as age, sex, and medical history. Treatment options for high uric acid levels include medications, dietary and lifestyle changes, hydration, avoiding alcohol, and treating underlying medical conditions. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or making significant dietary or lifestyle changes.